|
Nature of science:
Occam’s Razor: The Big Bang model was purely speculative until it was confirmed by the discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation. The model, while correctly describing many aspects of the universe as we observe it today, still cannot explain what happened at time zero. (2.7)
|
Understandings:
- The Big Bang model
- Cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation
- Hubble’s law
- The accelerating universe and redshift (z)
- The cosmic scale factor (R)
Applications and skills:
- Describing both space and time as originating with the Big Bang
- Describing the characteristics of the CMB radiation
- Explaining how the CMB radiation is evidence for a Hot Big Bang
- Solving problems involving z, R and Hubble’s law
- Estimating the age of the universe by assuming a constant expansion rate
|
International-mindedness:
- Contributions from scientists from many nations made the analysis of the cosmic microwave background radiation possible
Utilization:
- Doppler effect (see Physics sub-topic 9.5)
Aims:
- Aim 1: scientific explanation of black holes requires a heightened level of creativity
- Aim 9: our limit of understanding is guided by our ability to observe within our universe
|
Guidance:
- CMB radiation will be considered to be isotropic with T ≈ 2.76K
- For CMB radiation a simple explanation in terms of the universe cooling down or distances (and hence wavelengths) being stretched out is all that is required
- A qualitative description of the role of type Ia supernovae as providing evidence for an accelerating universe is required
Data booklet reference:
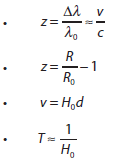
|
|