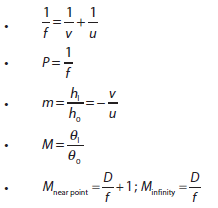Understandings:
- Thin lenses
- Converging and diverging lenses
- Converging and diverging mirrors
- Ray diagrams
- Real and virtual images
- Linear and angular magnification
- Spherical and chromatic aberrations
Applications and skills:
- Describing how a curved transparent interface modifies the shape of an incident wavefront
- Identifying the principal axis, focal point and focal length of a simple converging or diverging lens on a scaled diagram
- Solving problems involving not more than two lenses by constructing scaled ray diagrams
- Solving problems involving not more than two curved mirrors by constructing scaled ray diagrams
- Solving problems involving the thin lens equation, linear magnification and angular magnification
- Explaining spherical and chromatic aberrations and describing ways to reduce their effects on images
|
International-mindedness:
- Optics is an ancient study encompassing development made in the early Greco-Roman and medieval Islamic worlds
Theory of knowledge:
- Could sign convention, using the symbols of positive and negative, emotionally influence scientists?
Utilization:
- Microscopes and telescopes
- Eyeglasses and contact lenses
Aims:
- Aim 3: the theories of optics, originating with human curiosity of our own senses, continue to be of great value in leading to new and useful technology
- Aim 6: experiments could include (but are not limited to): magnification determination using an optical bench; investigating real and virtual images formed by lenses; observing aberrations
|