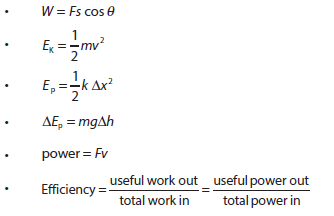|
Nature of science:
Theories: Many phenomena can be fundamentally understood through application of the theory of conservation of energy. Over time, scientists have utilized this theory both to explain natural phenomena and, more importantly, to predict the outcome of previously unknown interactions. The concept of energy has evolved as a result of recognition of the relationship between mass and energy. (2.2)
|
Understandings:
- Kinetic energy
- Gravitational potential energy
- Elastic potential energy
- Work done as energy transfer
- Power as rate of energy transfer
- Principle of conservation of energy
- Efficiency
Applications and skills:
- Discussing the conservation of total energy within energy transformations
- Sketching and interpreting force–distance graphs
- Determining work done including cases where a resistive force acts
- Solving problems involving power
- Quantitatively describing efficiency in energy transfers
Guidance:
- Cases where the line of action of the force and the displacement are not parallel should be considered
- Examples should include force–distance graphs for variable forces
|
Theory of knowledge:
- To what extent is scientific knowledge based on fundamental concepts such as energy? What happens to scientific knowledge when our understanding of such fundamental concepts changes or evolves?
Utilization:
- Energy is also covered in other group 4 subjects (for example, see: Biology topics 2, 4 and 8; Chemistry topics 5, 15, and C; Sports, exercise and health science topics 3, A.2, C.3 and D.3; Environmental systems and societies topics 1, 2, and 3)
- Energy conversions are essential for electrical energy generation (see Physics topic 5 and sub-topic 8.1)
- Energy changes occurring in simple harmonic motion (see Physics sub-topics 4.1 and 9.1)
|