Quadratic equations are the equations of degree 2 i.e the highest power of the variable is 2. Therefore it has 2 solution or 2 roots.
The standard form of a quadratic equation is
![]()
Where a, b, c are constant numbers, x is the variable and ![]() . Before deriving the general formula for a quadratic equation let us define the two terms.
. Before deriving the general formula for a quadratic equation let us define the two terms.
Discriminant of the quadratic equation (D)
![]()
note that ![]() for real roots of a quadratic equation
for real roots of a quadratic equation
Differential of a quadratic equation (Df)
The differential of quadratic equation ![]() is given by
is given by ![]() .
.
Now the quadratic formula is derived as ![]()
or,
![]()
Note that RHS has two signs(+ and -), so it will give us the two roots which are the two solutions of the quadratic equation
Example 1
![]()
Here ![]()
![]()
![]()
Discriminant ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Differential Df ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Putting in Quadratic formula
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
Hence ![]() or
or ![]() are the required solution or roots of the given equation.
are the required solution or roots of the given equation.
Example 2
![]()
Here ![]()
![]()
![]()
Discernment ![]()
![]()
![]()
Differential Df ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Substitute in Quadratic formula
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]() or
or 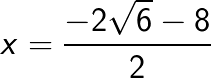
i.e ![]() or
or ![]() are the required solutions
are the required solutions
Example 3
![]()
Here ![]()
![]()
![]()
Discernment ![]()
![]()
![]()
Differential ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Substituting in Quadratic formula
![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
So here both the solution are same (coincide) ![]() ,beacuse discriminant D = 0
,beacuse discriminant D = 0
Example 4
![]()
here ![]()
![]()
![]()
Discriminant ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Here ![]() as
as ![]() so on real solution or roots are possible for this equation, so we need not proceed further.
so on real solution or roots are possible for this equation, so we need not proceed further.
Exercise Solution
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
Corollary
Special types of quadratic equations which are of Reciprocal type can be solved by observation (Vilokanam) only.
Example 1
![]()
LHS is of reciprocal type so we have to break the RHS into two Reciprocal types
![]()
By comparing on both sides we can observe that ![]() or
or ![]() are the required solutions.
are the required solutions.
Example 2
![]()
![]()
So, X = 9 or X= 1/9
Example 3
![]()
![]()
Here ![]() or
or ![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
![]() or
or 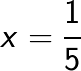 are
are
The two required solutions (note here that ![]() and
and ![]() are the reciprocal in LHS)
are the reciprocal in LHS)
Exercise Solution
![]() X=5 or X=1/5
X=5 or X=1/5
![]() X=7 or X=1/7
X=7 or X=1/7
![]() X=8 or X=-1/8
X=8 or X=-1/8
![]() X = -11/5 or x = -4/5
X = -11/5 or x = -4/5
![]()
![]() or
or ![]()
Course:


