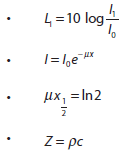Understandings:
- Detection and recording of X-ray images in medical contexts
- Generation and detection of ultrasound in medical contexts
- Medical imaging techniques (magnetic resonance imaging) involving nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
Applications and skills:
- Explaining features of X-ray imaging, including attenuation coefficient, half-value thickness, linear/mass absorption coefficients and techniques for improvements of sharpness and contrast
- Solving X-ray attenuation problems
- Solving problems involving ultrasound acoustic impedance, speed of ultrasound through tissue and air and relative intensity levels
- Explaining features of medical ultrasound techniques, including choice of frequency, use of gel and the difference between A and B scans
- Explaining the use of gradient fields in NMR
- Explaining the origin of the relaxation of proton spin and consequent emission of signal in NMR
- Discussing the advantages and disadvantages of ultrasound and NMR scanning methods, including a simple assessment of risk in these medical procedures
|
International-mindedness:
- There is constant dialogue between research clinicians in different countries to communicate new methods and treatments for the good of patients everywhere
- Organizations such as Médecins Sans Frontières provide valuable medical skills in parts of the world where medical help is required
Theory of knowledge:
- “It’s not what you look at that matters, it’s what you see.” – Henry David Thoreau. To what extent do you agree with this comment on the impact of factors such as expectation on perception?
Utilization:
- Scanning the human brain (see Biology sub-topic A.4)
|