Understandings:
- Period, frequency, angular displacement and angular velocity
- Centripetal force
- Centripetal acceleration
Applications and skills:
- Identifying the forces providing the centripetal forces such as tension, friction, gravitational, electrical, or magnetic
- Solving problems involving centripetal force, centripetal acceleration, period, frequency, angular displacement, linear speed and angular velocity
- Qualitatively and quantitatively describing examples of circular motion including cases of vertical and horizontal circular motion
Guidance:
- Banking will be considered qualitatively only
Data booklet reference:
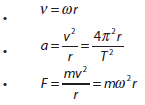
|
International-mindedness:
- International collaboration is needed in establishing effective rocket launch sites to benefit space programmes
Theory of knowledge:
- Foucault’s pendulum gives a simple observable proof of the rotation of the Earth, which is largely unobservable. How can we have knowledge of things that are unobservable?
Utilization:
- Motion of charged particles in magnetic fields (see Physics sub-topic 5.4)
- Mass spectrometry (see Chemistry sub-topics 2.1 and 11.3)
- Playground and amusement park rides often use the principles of circular motion in their design
Aims:
- Aim 6: experiments could include (but are not limited to): mass on a string; observation and quantification of loop-the-loop experiences; friction of a mass on a turntable
- Aim 7: technology has allowed for more accurate and precise measurements of circular motion, including data loggers for force measurements and video analysis of objects moving in circular motion
|